Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing offers and services, similar to waiters, storehouses, databases, networking, software, and analytics, over the Internet on a pay- as- you- go base. rather than retaining and maintaining physical waiters and data centers, druggies can pierce computing offers and services from a pall provider.
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing offers and services, similar to waiters, storehouses, databases, networking, software, and analytics, over the Internet on a pay- as- you- go base. rather than retaining and maintaining physical waiters and data centers, druggies can pierce computing offers and services from a pall provider.
Cloud computing provides several benefits, including
Scalability
The cloud allows businesses to snappily and fluently gauge their computing coffers up or down as demanded, without the need to invest in a fresh tackle.
Cost Savings
Cloud eliminates the need for businesses to invest in and maintain precious- demesne IT structures. This can affect in significant cost savings.
Inflexibility
Cloud computing provides businesses with lesser inflexibility in terms of where, when, and how they pierce calculating coffers.
trustability
Cloud providers generally have multiple data centers in different geographic locales, which helps ensure that data and operations remain available indeed in the event of a localized dislocation.
Security Cloud calculating providers generally have robust security measures in place to cover data and operations from cyber pitfalls.
There are three main types of cloud computing services:
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS): This provides virtualized computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking, that users can rent on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS): This provides a platform for developers to build, test, and deploy software applications without having to manage the underlying infrastructure.
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS): This provides access to software applications that are hosted by a third-party provider and accessed over the Internet.
type Cloud Computing
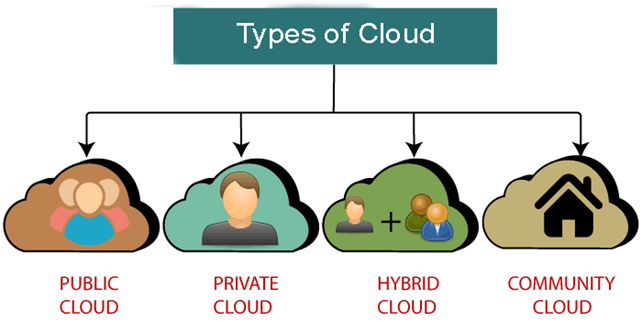
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): This type of cloud provides virtualized computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networks, over the internet. Customers can rent these resources on-demand, paying only for what they use.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): This type of cloud provides a platform for developing, testing, and deploying applications over the internet. PaaS providers offer a variety of tools and services, such as development frameworks, databases, and application hosting environments.
Software as a Service (SaaS): This type of cloud computing provides access to software applications over the internet, without the need to install or maintain software on local devices. SaaS applications are typically delivered through a web browser, and users pay a subscription fee to access the software.
Hybrid cloud: This type of cloud computing combines public and private cloud services, allowing organizations to use both on-premises infrastructure and cloud-based resources as needed.
Function as a Service (FaaS): This is a type of cloud computing that allows developers to create and run small pieces of code, called functions, in response to specific events or triggers. FaaS is also known as serverless computing because developers do not need to worry about managing the underlying infrastructure.
Desktop as a Service (DaaS): This type of cloud computing provides virtual desktops that can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection. DaaS allows organizations to provide employees with a consistent desktop experience, regardless of the device they are using.
Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS): This type of cloud computing provides backup and recovery services in the event of a disaster, such as a natural disaster, cyberattack, or hardware failure. DRaaS allows organizations to quickly restore critical data and systems and minimize downtime.
Big Data as a Service (BDaaS): This type of cloud computing provides tools and services for managing and analyzing large datasets. BDaaS providers offer a variety of services, such as data storage, data processing, and data analysis, to help organizations make sense of their data.
Internet of Things (IoT) as a Service: This type of cloud computing provides a platform for managing and analyzing data from IoT devices, such as sensors, wearables, and smart appliances. IoT as a Service providers offer a variety of services, such as data storage, data processing, and analytics, to help organizations make sense of their IoT data.


nice