Blockchain
Blockchain is a digital technology that allows for secure, transparent, and decentralized record-keeping. It’s a type of distributed tally that allows multiple parties to store and pierce information in a way that’s secure, tamper- evidence, and empirical.
The technology has multitudinous implicit operations, including in finance, force chain operation, advancing systems, identity verification, and more. It has the implicit to ameliorate translucency, effectiveness, and security in a wide range of diligence, while also reducing the need for interposers and centralized authorities.
New deals are validated by the network of computers and added to the tally in the form of” blocks”. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the former block, creating a” chain” of blocks that can not be altered without also altering all posterior blocks in the chain.
Because the tally is distributed across multiple computers, it’s extremely delicate to tamper with or alter the data on a blockchain. This makes blockchain technology largely secure and resistant to fraud or hacking.
Type of Blockchain
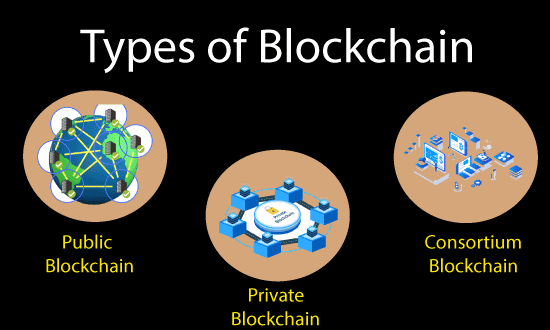
public, private, and hybrid.
Public:- A public blockchain is a decentralized network where anyone can join and share in the network. The data on the blockchain is fully public and transparent, and all actors have equal access and control over the network. exemplifications of the public include Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Private:- A private blockchain is a permissioned network where only authorized parties can join and share in the network. The data on the blockchain isn’t public and is only accessible to authorized actors. Private blockchains are frequently used by companies or associations for internal record-keeping or force chain operations. exemplifications of private blockchains include Hyperledger Fabric and Corda.
mongrel:- A mongrel blockchain is a combination of both public and private blockchains. It allows for both public and private bumps to share in the network and can give a position of translucency and sequestration that isn’t possible with either type alone. exemplifications of mongrels include Dragonchain and Kadena.
there are also other variations and subcategories, similar to institute blockchains( which are governed by a group of associations), sidechains( which are separate blockchain networks that can interact with a main blockchain), and more. Each type of blockchain has its own strengths and sins, and the choice of which type to use depends on the specific requirements and conditions of the operation or system being developed.
Uses of Blockchain
Cryptocurrencies: One of the most well-known uses of blockchain technology is the creation of cryptocurrencies, similar to Bitcoin and Ethereum. Blockchain enables secure and decentralized digital deals without the need for interposers like banks.
Supply Chain Management: can be used to produce a transparent and secure force chain operating system. The technology can help track the movement of goods from the point of origin to the point of consumption, reducing fraud, crimes, and inefficiencies.
Identity Verification: can be used to produce a decentralized and secure identity verification system. This can help identity theft and fraud, and give individualities further control over their particular data.
Voting Systems: can be used to produce secure and transparent voting systems. The technology can help ensure that votes are counted directly and that the results aren’t tampered with.
Smart Contracts: can be used to produce tone-executing contracts that automatically apply the terms of the agreement. This can help reduce the need for interposers and increase the effectiveness and translucency of contractual agreements.
Healthcare: can be used to create a secure and decentralized system for storing and sharing medical records. This can help improve the quality of healthcare by providing doctors and healthcare providers with access to complete and accurate patient information.
Real Estate: Blockchain can be used to create a secure and transparent system for property transactions. The technology can help reduce fraud and errors, and make it easier for buyers and sellers to transact with each other directly.
Banking and Finance: can be used to create a more efficient and secure banking and financial system. It can help reduce fraud and errors, increase transparency, and improve the speed and efficiency of transactions.
Digital Identity: can be used to create a decentralized and secure digital identity system. This can help individuals manage their digital identities more easily and securely, while also providing businesses and organizations with a reliable way to verify the identities of their customers.
Intellectual Property: can be used to create a decentralized and secure system for managing and protecting intellectual property. This can help prevent copyright infringement, reduce the cost of enforcing intellectual property rights, and make it easier for creators to monetize their work.
Gaming: can be used to create a more secure and transparent gaming ecosystem. It can help prevent cheating, reduce fraud, and provide players with more control over their in-game assets.
Energy: can be used to create a decentralized and transparent system for managing energy transactions. This can help reduce the cost of energy transactions, increase efficiency, and encourage the adoption of renewable energy sources.
Insurance: can be used to create a more efficient and transparent insurance system. It can help reduce fraud, increase transparency, and improve the speed and efficiency of claims processing.